What is hexadecimal?
You might be able to tell from the name that hexadecimal (hex = 6 and dec = 10) means a base-16 number system. Just like binary and denary this means that each place value is worth 16 times are much as we go from right to left.
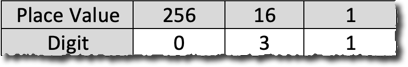
If the digits are between 0 and 9 then hexadecimal looks like denary so we would write this number as 3116 to make it clear that we using base-16. If we go above the digit 9 then the letters A – F are used to represent the digits.
| Denary Digit | Hexadecimal Digit |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 |
| 7 | 7 |
| 8 | 8 |
| 9 | 9 |
| 10 | A |
| 11 | B |
| 12 | C |
| 13 | D |
| 14 | E |
| 15 | F |
Why Hexadecimal?
There are two different parts to this:
- Why use hexadecimal rather than any other number base?
- What advantages does hexadecimal offer over binary?
Why hexadecimal?
Computers store all data in binary, 1 binary digit (a bit), is a really small amount of memory. Computer memory is organised into groups a 8 bits and these groups are called bytes. A single bit can hold either a 0 or a 1
How much can we store?
| Amount of memory | What can be stored? | ||
| 1 bit | |||
| 2 bits | |||
| 3 bits | |||
| 4 bits | |||
| 5 bits | |||
| 6 bits | |||
| 7 bits | |||
| 8 bits (1 bytes) | |||
| 16 bits | |||
| 32 bits |
Converting from binary to hexadecimal
Binary is the only thing computers understand but as humans we find binary difficult to deal with. Binary numbers tend to be quite long (lots of digits) and this makes noticing errors and remembering the number quite difficult.
Hexadecimal is a useful number system because it is easy to convert between binary and hexadecimal so computer scientists often prefer it. This is simply about making things easy for people, computers still only deal with binary.

When you hear the phrase "computers only use binary" we're talking about down at the level of the processor. Fortunately modern computer operating systems are very human friendly and allow us to enter data in lots of different ways. However as a Computer Science Student you should always be aware that ultimately everything that the CPU does is done in binary.
Converting a binary number to hexadecimal
As a computer science student you will make use of hexadecimal and you will be expected to be able to convert between binary and hexadecimal. The process of mostly easy which is why hexadecimal is so useful in this subject.
- Split the binary number into groups of 4 digits
- Write the place values above each group of 4 digits (8 4 2 1)
- Multiply each binary digital value (0 or 1) by its place value (8,4,2 or 1)and add up the results
- For results between 0 and 9 nothing else to do
- For results between 10 and 15 convert to the hexadecimal digit:
- 10 = A
- 11 = B
- 12 = C
- 13 = D
- 14 = E
- 15 = F
- Repeat this for each group of 4 digits
The process of converting from binary to hexadecimal is shown in this video: